栈
栈是一种只能在一端进行插入或删除操作的线性表。
栈的结构
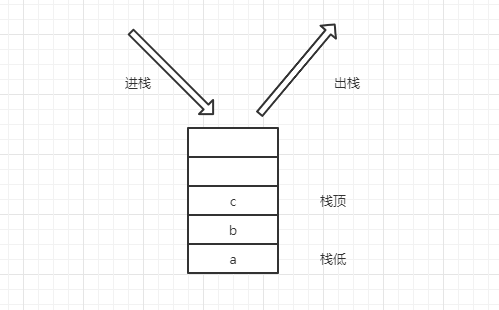
栈顶和栈低
栈分为栈顶和栈低。
栈顶:数据插入和删除的地方,也就是说栈顶是动态的,随着插入和删除操作数据变化而变化。
栈低:栈的底端。
出栈和进栈
插入操作被称为 进栈。
删除操作被称为 出栈。
后进先出原则
栈遵循着后进先出原则。如图所示:a、b、c依次进栈,然后如果执行出栈操作那么必然先出栈 c,再到b 和 a,而不能直接跳过 c 直接出栈 b 和 a。
栈的实现
栈中数据元素的逻辑关系呈线性关系,所以栈可以像线性表一样采用顺序结构进行存储。所以实现栈的方式也分为两种:一种采用数组实现的顺序结构,一种为链式实现的栈式结构。
栈的顺序存储结构实现
js
class Stack {
constructor(n) {
this.data = new Array(n)
this.top = -1
}
isEmpty() { // 判断栈是否为空
return this.top === -1
}
push(value) { // 进栈
if(this.top == this.data.length - 1) { // 栈满
return false
}
this.top++
this.data[this.top] = value
return true
}
pop(value) {
if(this.top === -1) { // 栈空
return false
}
this.top--
return true
}
getTop() { // 取栈顶元素
if(this.top === -1) { // 栈空
return false
}
let res = this.data[this.top]
return res
}
}使用数组来存储数据,再添加一个变量 top 来充当指针,指向当前栈顶的位置。每次进栈就是 top+1,出栈就使 top-1。
栈的链式结构
首先实现链表的结点
js
class Node {
constructor(value, next = null) {
this.value = value
this.next = next
}
}接着实现栈的链式结构。由于栈的特点是后进先出的原则,所以需要采用头插法。删除结点也需要改成删除首结点,以达到删除后进的结点。
js
class Stack {
constructor() {
this.node = new Node() // 新建一个头结点
}
isEmpty() {
return this.node.next == null
}
push(node) { // 头插法
node.next = this.node.next
this.node.next = node
}
pop() {
if(this.isEmpty()) return false
this.node.next = this.node.next.next
return true
}
getTop() { // 取栈顶元素
return this.node.next
}
dispLink() {
let linkNode = this.node.next
while(linkNode) {
console.log(linkNode.value)
linkNode = linkNode.next
}
}
}